This blog is co-authored with Mason Yan, Partner Solution Architect from Wiz.
Table of Contents
Summary
Wiz helps organizations secure everything they build and run in their cloud environments. Wiz Defend is Wiz’s real-time cloud detection and response solution, designed to identify, investigate, and contain security threats across cloud environments. It provides cross-layer threat detection by analyzing data from cloud control planes, SaaS, identity providers (IdPs), workloads, and networks.
In this blog, we will describe how you can leverage Wiz Defend and its advanced threat detection, automated investigation and incident response & containment capabilities to detect and respond to your Google Cloud security threats..
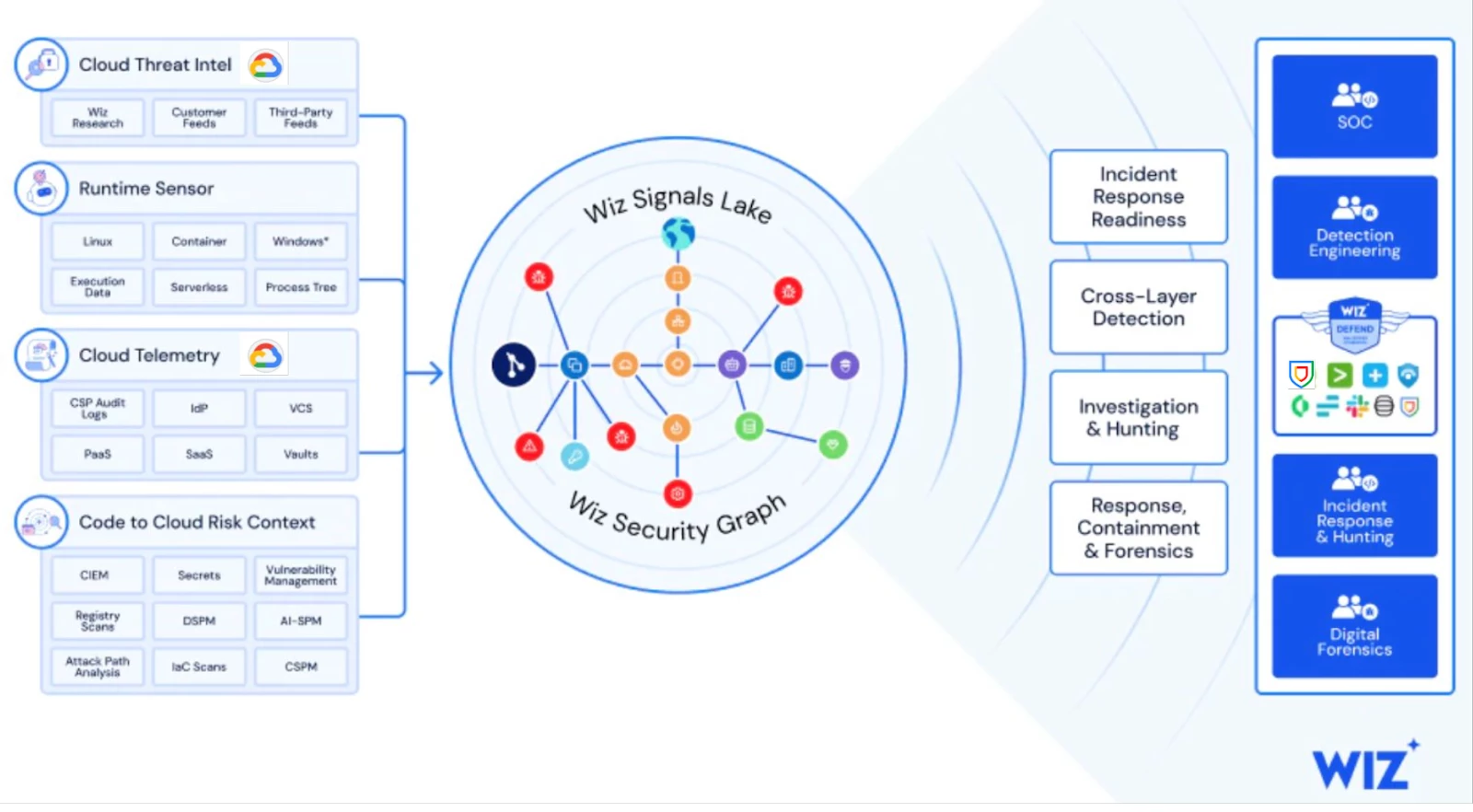
For more information about Wiz and Google Cloud, see the Wiz website and the Wiz solutions on Google Cloud.
Architecture
The following diagram shows how Wiz connects to your Google Cloud environment and how Wiz Cloud and Wiz Defend is integrated with Google Cloud.
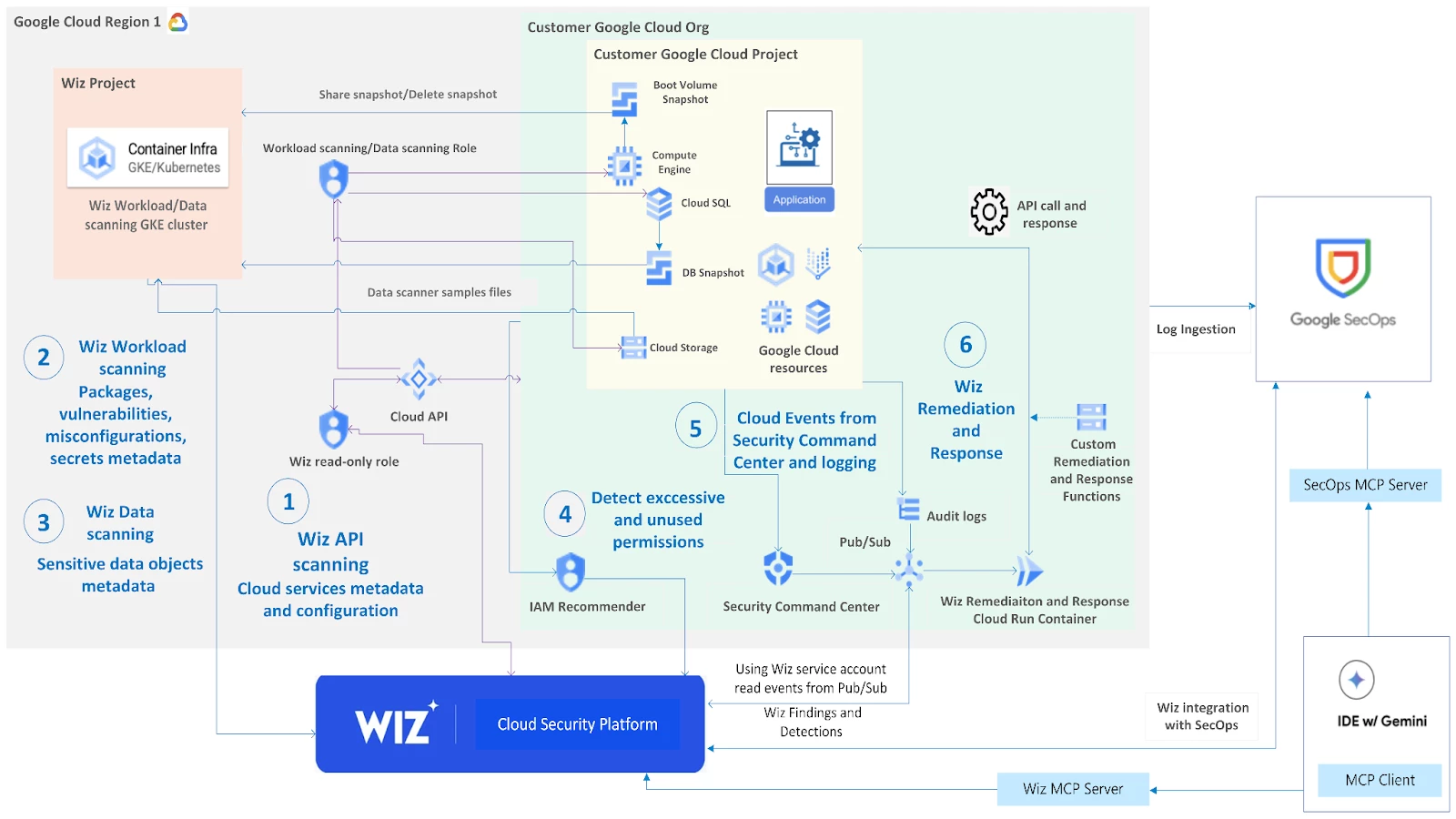
Wiz Cloud Security Platform is a software-as-a-service (SaaS) solution. This architecture diagram demonstrates the following workflow:
- Wiz API scanning collects Google Cloud services and their configuration metadata to build a complete inventory.
- Wiz Workload scanning collects the metadata of operating systems, apps, packages, secrets, and container files to create a list of vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
- Wiz Data scanning scans Google Cloud Storage, non-OS volumes, tables in Google Cloud SQL, and collects metadata from sensitive data objects.
- Wiz uses Google Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM) Recommender to find excessive and unused permissions to create Wiz findings.
- Wiz ingests Google Cloud Admin Activity audit logs and Google Security Command Center findings to add threat events to create Wiz findings.
- Wiz Remediation and Response provides simple workflows for fixing common cloud misconfigurations and security risks. Wiz fixes these misconfigurations using standard cloud provider API calls, in a manual, semi-automated or fully-automated method.
- Wiz Findings and threat Detections are sent to a Pub/Sub topic
- A Cloud Run instance is subscribed using a push subscription to have the message delivered to the Wiz Remediation and Response container running in Cloud Run. Cloud Run runs a pre-built Wiz remediation container image with all required libraries and out-of-the-box functions included.
- The response function is triggered. A native Google Cloud API call is constructed to perform the remediation task and passed to the Google Cloud management plane for action. Optionally, custom functions may be read in from a custom functions storage bucket
The Wiz and Google Security Operations integration enhances the effectiveness of Security Operations Center (SOC) teams in managing cloud-native threats. The new enhanced version of the integration will cover broader SecOps use cases.
On the AI Integration side and specifically on MCP (Model Context Protocol), in the effort to foster an open and and interoperable AI security ecosystem, Wiz has released the MCP server which can seamlessly translates plain-language queries into Wiz-specific operations, such as querying resources, assessing risks, and retrieving data from third-party security tools.
When customer uses their MCP client of choice such as Gemini Code Assist with Wiz MCP Server in conjunction with Google Security Operations MCP server, this will enable the user to perform tasks such as searching security events, retrieving alerts, looking up entity information (IPs, domains, hashes), and listing security rules within the Google Security Operations platform, enable case management, playbook actions, and orchestration of security workflows. The Wiz MCP Server is available today as a standalone local run package, and Wiz is working with Google Cloud to bring the MCP server to Google Marketplace and make it available for the customers.
Connect Wiz Defend to Your Google Cloud
Create a Google Cloud connector
Before you connect Wiz to your Google Cloud infrastructure, ensure that you've met the following prerequisites. To deploy on the organization level, the person who performs the connection must have sufficient permissions, either as a Google Cloud owner or as a user with the following organization-level roles:
roles/iam.serviceAccountAdmin
roles/iam.organizationRoleAdmin
roles/iam.securityAdminNote: Wiz strongly recommends that you connect on the organization level. Doing so lets all Google Cloud projects, both existing and future, be detected and scanned automatically.
To deploy on the project level, the person who performs the connection must have the rights of a Google Cloud project role/owner role (or better).
Other prerequisites include the following:
- Google Cloud: Obtain your Google Cloud organization or project ID if you are only deploying Wiz on the project level; Make sure you have the permissions to enable Google API services
- Wiz: Have Global Admin, Global Contributor, Settings Admin, or Connector Admin access to Wiz platform
For detailed steps on connecting Wiz to Google Cloud, see the Wiz documentation on How to connect to Google Cloud
Connect Cloud Audit Logs to Wiz Defend
Connecting Wiz to your Google Cloud event logs enables the following features on Wiz:
- Cloud events & detections—Detect security events that may indicate an ongoing breach or violation of your organizational security policies, and generate Issues that can in turn trigger Automation Rules.
- Near real-time scanning—Deliver near real-time visibility by scanning a resource or types of resources based on a specific cloud event, updating their Graph objects, and assessing them for misconfigurations.
Wiz ingests cloud events from Google Cloud audit logs and Google Workspace audit logs. These logs are streamed to a Pub/Sub topic that you create.
Here are the deployment steps:
- Create a Pub/Sub topic and subscription in your Google Cloud project.
- Stream admin activity and data access audit logs to the created topic.
- Stream audit logs from Google Cloud to Wiz.
- Connect Wiz to the Pub/Sub topic.
For more information about configuration details, see the Wiz documentation on Connect to GCP Cloud Events.
Deploy Wiz Runtime Sensor on Kubernetes and Linux
The Wiz Runtime Sensor is a Linux-based executable that provides visibility into runtime workloads in cloud and on-premises environments. Once deployed, the Runtime Sensor monitors all processes and containers on all nodes. This allows it to validate vulnerabilities in runtime and detect threats in real time. The Runtime Sensor reports its detections back to Wiz, where they are represented as cloud events, enriched with details on all relevant entities.
The Runtime Sensor uses eBPF to monitor the system state. It is lightweight in memory and compute footprint, and designed to be maximally compatible and non-disruptive to modern production workloads.
Runtime Sensor will need outbound connectivity to the Wiz backend at https://auth.app.wiz.io so if you have firewall policies please make sure it is allowed.
- The Runtime Sensor can be installed on Google Cloud Kubernetes Engine cluster. It is deployed as a DaemonSet. Once deployed, it monitors all containers and processes on the node and performs runtime analysis. For more details, see the Wiz documentation on Install Runtime Sensor for Kubernetes.
- The Runtime Sensor can also be installed on Linux hosts, either as a native binary using the package manager of your choice or within a container. For more details, see the Wiz documentation on Install Runtime Sensor for Linux.
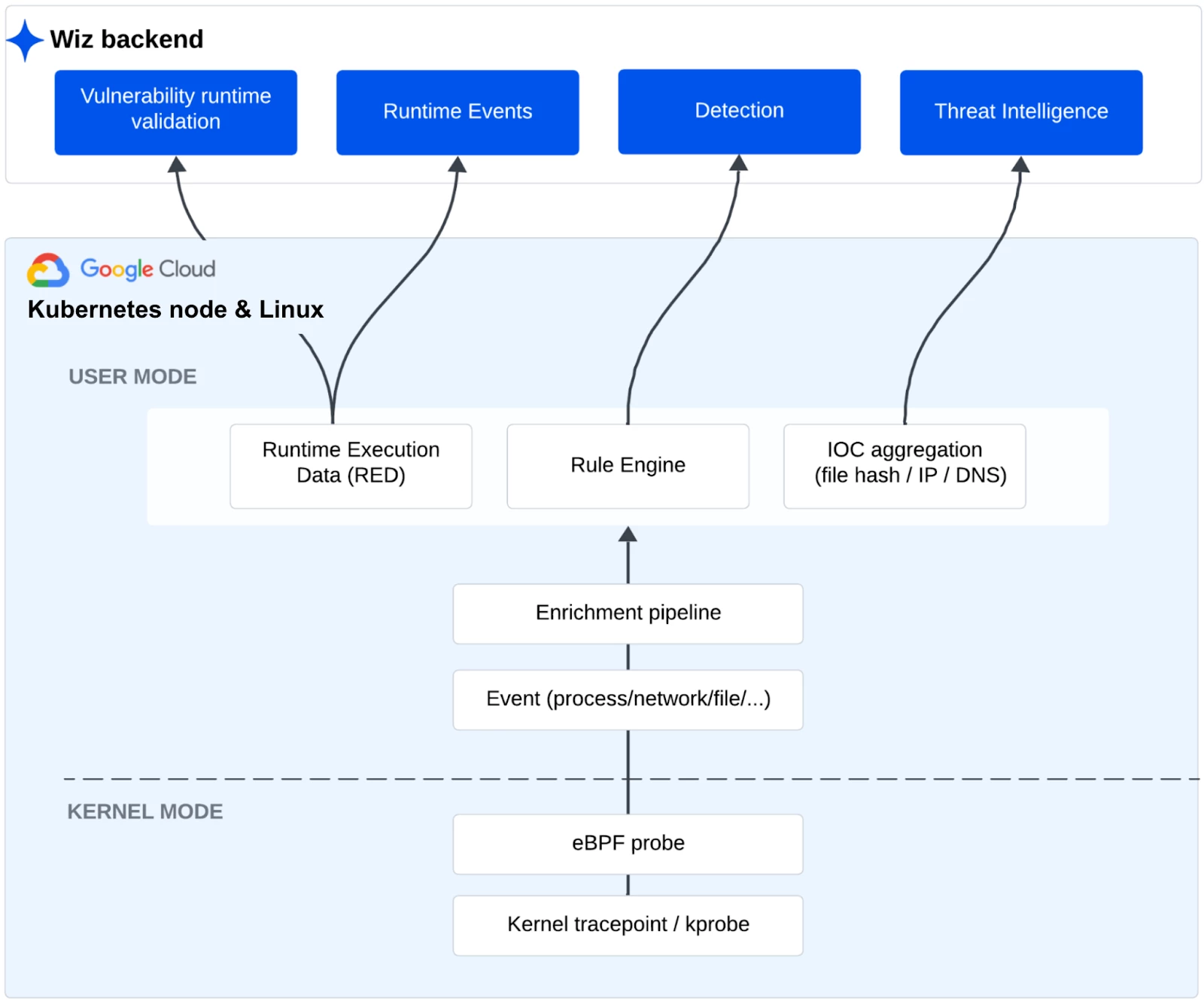
Figure: The Wiz Runtime Sensor Architecture in GCP Cloud
Configure Wiz Remediation & Response in Google Cloud
When configuring Remediation & Response in Google Cloud, Wiz will deploy infrastructure services and IAM roles in the customer Google Cloud tenant. It consists of two parts:
- Infrastructure services—requires Cloud Run, Pub/Sub; optional Cloud Storage
- Remediation worker role—provides IAM permissions to Cloud Run to act on the account(s)
Figure: Cloud Run Container deployed in customer tenant
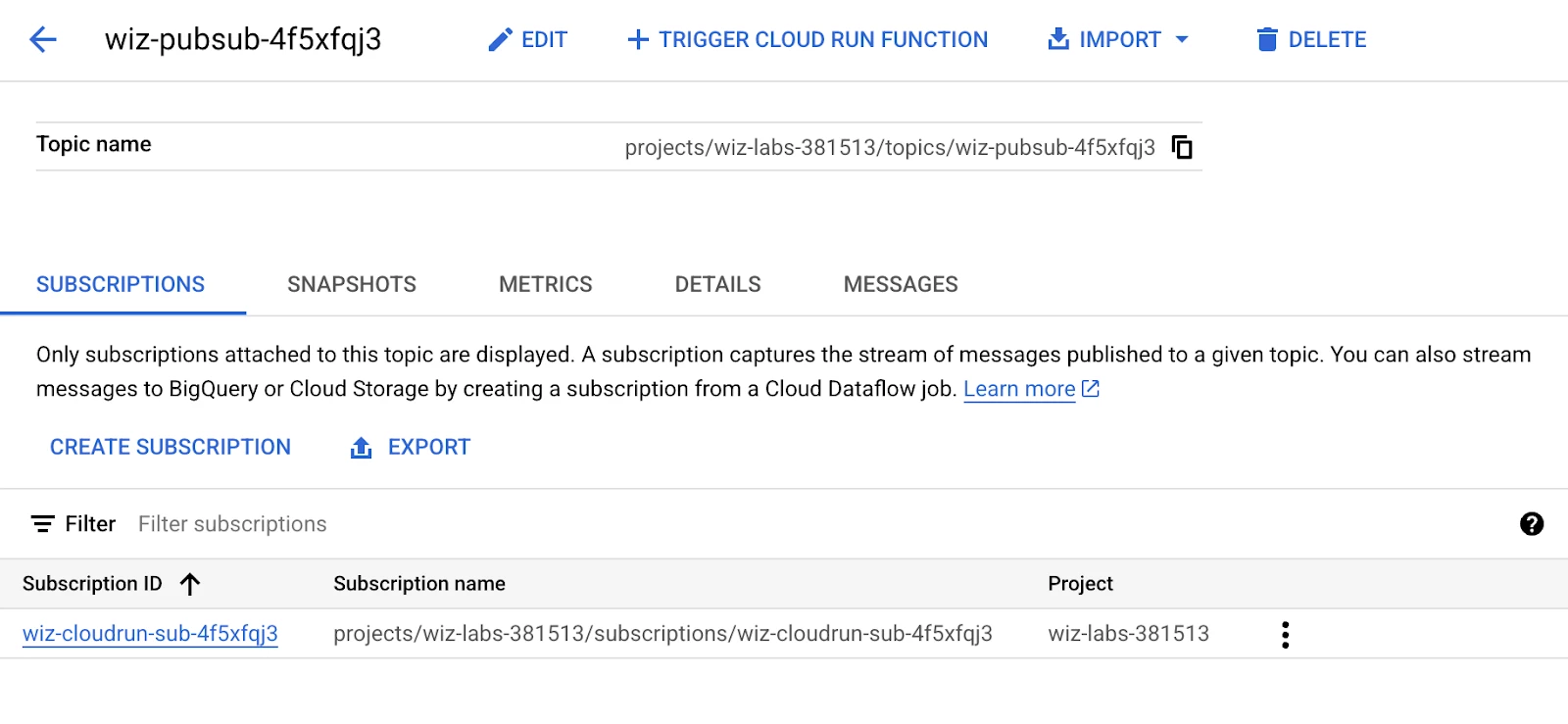
Figure: Cloud Pub/Sub Topic and Subscription in customer tenant
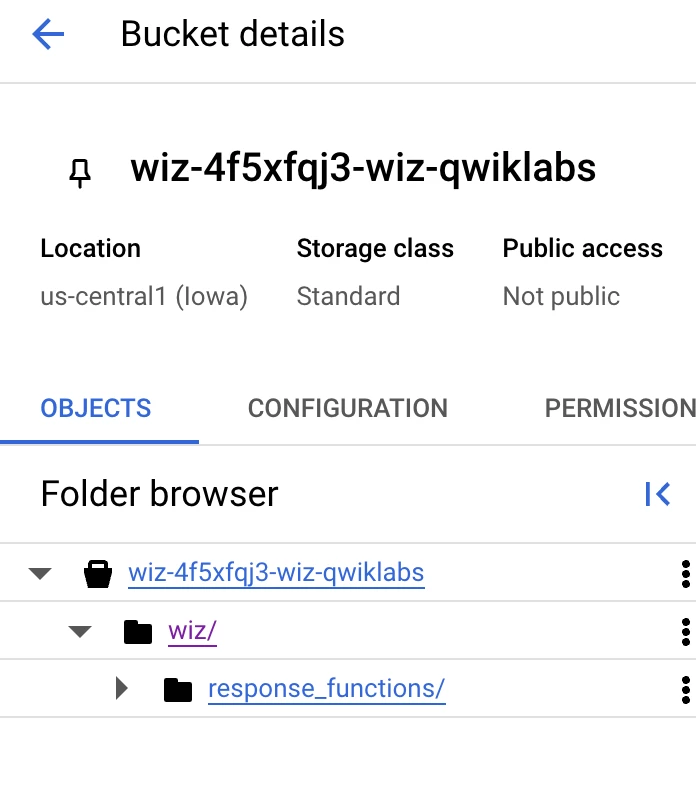
Figure: Cloud Storage that stores user-defined response functions
Security
Required Roles by Wiz Defend
For Wiz Defend to work properly in your Google Cloud environment, it will need to create both read only roles for detection and writable roles for executing remediation actions in Google Cloud. For details of the read only roles, see Wiz doc here
For the writable permissions, Wiz will require the following Google Cloud IAM permissions:
- Pub/Sub publisher IAM role. This is used by Wiz to publish event messages from the Wiz back end to the Pub/Sub topic in Google Cloud and uses the Pub/Sub Publisher built in role.
- A Cloud Run service account that is responsible for invoking Cloud Run and performing remediation on the respective resources.
For more detailed explanation on how these roles are leveraged by Wiz, see
Required roles in Wiz documentation.
Remediation Container Image
In addition to the required roles above, Remediation and Response are supplied in a Wiz container image that is published on Google Cloud Artifact Registry (us-docker.pkg.dev).
The Wiz container image has the following main components:
- Wiz remediation core package (wiz_remediation.core). This package contains foundational features such as custom bucket downloader, event logging and supporting mechanism for Wiz Defend.
- Wiz remediation Google Cloud specific package (wiz_remediation.gcp). This package processes the incoming event from Wiz and executes the mapped response function. It also has Google Cloud API calls to the custom functions bucket and for labelling modified resources with the AutoTag feature.
- Built-in response functions for Google Cloud. These functions are installed as part of the wiz_remediation.gcp package and require no further configuration.
From a security perspective, the Wiz container image has a very small footprint, a high cadence of updated releases, and is signed by Cosign, SBOM, SLSA 1.0 provenance attestation and a reduced risk of known vulnerabilities.
Custom Remediation Functions on Google Cloud
There may be use cases when you want to add the capability beyond what the Wiz-provided remediation functions do. It is possible to do so by creating your own custom response functions in Wiz. For this, create a Cloud Storage bucket for hosting the response functions. This dedicated bucket keeps your custom functions separate from the Cloud Run instance and preserves the customizations during a Wiz Remediation container image update. It also leverages Cloud Storage features such as versioning, encryption, auditing, soft delete, and high availability.
Custom Functions are written in Python 3.12+ and stored in the Cloud Storage Bucket that is the language binary major version supplied in the Wiz Remediation container image. The Wiz image has already included Google Cloud Python Cloud Client Libraries as well as the standard libraries included with Python for the convenience of the developer.
When the Wiz Cloud Run instance is triggered by a message it receives from the Pub/Sub topic, it queries the configured custom functions in the Cloud Storage bucket. If custom function content is detected in the Cloud Storage bucket, it is copied into the running container instance and processed by the Remediation and Response engine. As mapped custom functions are triggered from Wiz, the corresponding custom function is executed within the container.
The Cloud Storage custom functions bucket is queried every time the container instance is triggered, so that all current content is processed and any updated custom functions are immediately copied over and made available.
The use of Cloud Storage offers multiple advantages: the custom functions are preserved when the Wiz container image is updated; the bucket permissions can be tailored granularly for security reasons, and Cloud Storage versioning can help maintain copies of older versions in case of rollback.
For more detailed information, see Wiz documentation on Create Custom Response Functions for Google Cloud and Add custom response functions storage.
Use Case 1: Detecting and Containing a compromised GCE instance in customer Vertex AI Workloads
This use case highlights a cryptomining attack on Vertex AI infrastructure, where Google Compute Engine (GCE) instances, a critical component of Vertex AI, were targeted for unauthorized cryptojacking. Cloud workloads, including GCE instances, are prime targets for attackers seeking to exploit compute resources for illicit cryptomining operations.
In this scenario, the compromised GCE instance had access to AI training data, posing serious risks such as data loss, model poisoning, and integrity compromise. An attacker leveraging unauthorized access could manipulate datasets, skew AI model outcomes, or exfiltrate sensitive information.
Without real-time threat detection and automated response mechanisms, cryptojacking attacks can escalate, leading to operational cost surges, performance degradation, and potential data exposure. Proactively securing AI infrastructure is crucial to preventing such risks and maintaining the integrity of cloud-based machine learning environments.
Threat Detection
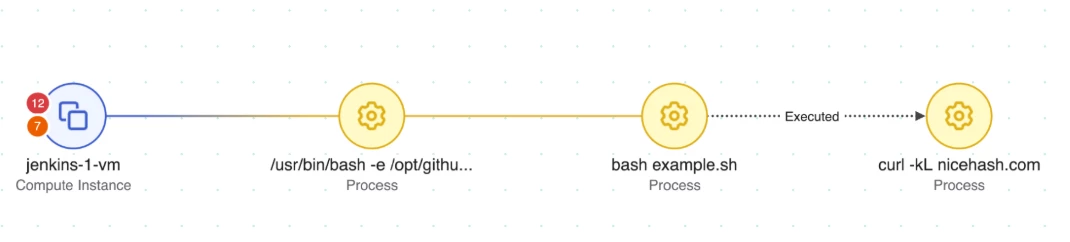
In this use case, Wiz Defend detected and raised a high-severity alert when a Google Cloud Compute Instance (jenkins-1-vm) exhibited suspicious behavior:
- The instance repeatedly executed /usr/bin/curl to connect to nicehash.com, a domain associated with cryptomining operations.
- Multiple high-severity alerts were generated due to persistent outbound requests, indicating possible unauthorized resource usage.
- Wiz Runtime Sensor flagged the activity as a potential cryptojacking incident, highlighting the risk of malware deployment and financial impact.
Investigation & Threat Analysis
Using Wiz Defend’s Investigation Graph and Threat Timeline, security teams gained full visibility into the attack sequence:
- The Investigation Graph mapped out the processes, IP origins, and affected cloud resources, enabling efficient root cause analysis.
- The Threat Timeline provided an interactive event sequence, highlighting key attack stages and potential privilege escalation paths.
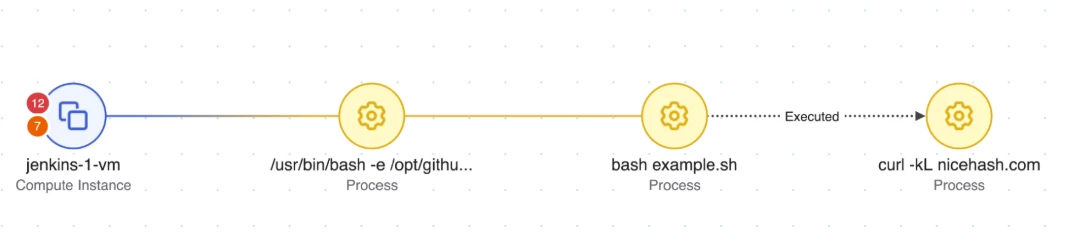
Figure: Investigation Graph
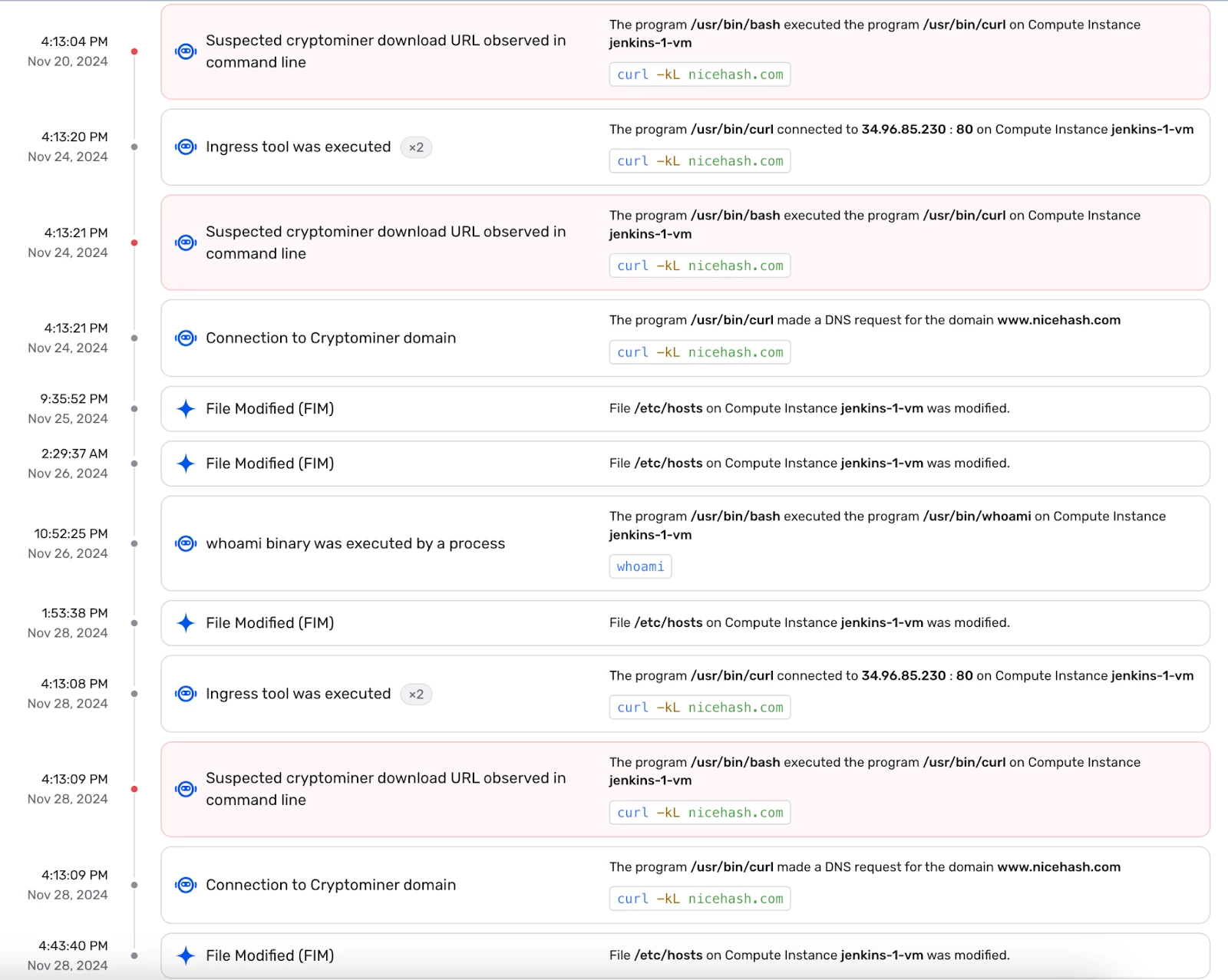
Figure: Threat Timeline
Response & Remediation
To mitigate the threat and prevent further impact, Wiz Defend offers one-click response actions. For example, the code below demonstrates how the compromised GCE instance can be stopped.
"""
Required Permissions:
- compute.instances.get
- compute.instances.stop
"""
from google.cloud.compute_v1 import InstancesClient
import google.auth
from wiz_remediation_core.logger import Logger
from wiz_remediation_core.response_function_api import GCPRemediationArgs, RemediationResult
from wiz_remediation_gcp.response_functions.common import LONG_TIMEOUT, SHORT_TIMEOUT
def remediate(args: GCPRemediationArgs) -> RemediationResult:
credentials, _ = google.auth.default()
client = InstancesClient(credentials=credentials)
logger = Logger(loglevel='info')
logger.info(f"Stopping Virtual Machine {args.target_resource.resource_name}")
splitted_id = args.target_resource.resource_id.split('/')
if splitted_id[-4] != "zones":
return RemediationResult.fail(f"Invalid resource id: {args.target_resource.resource_name}")
zone = splitted_id[-3]
existing_vm = client.get(project=args.target_resource.project_id,
instance=args.target_resource.resource_name,
zone=zone,
timeout=SHORT_TIMEOUT)
if is_remediated(existing_vm):
return RemediationResult.success(
f"Virtual Machine {args.target_resource.resource_name} was already stopped.")
client.stop(project=args.target_resource.project_id,
instance=args.target_resource.resource_name,
zone=zone).result(timeout=LONG_TIMEOUT * 5)
updated_vm = client.get(project=args.target_resource.project_id,
instance=args.target_resource.resource_name,
zone=zone,
timeout=SHORT_TIMEOUT)
assert is_remediated(updated_vm)
logger.info(f"Stopped Virtual Machine: {args.target_resource.resource_name}")
return RemediationResult.success(f"Virtual Machine {args.target_resource.resource_name} was stopped successfully.")
def is_remediated(vm) -> bool:
return vm.status == "TERMINATED" or vm.status == "STOPPING" or vm.status == "STOPPED"
if __name__ == '__main__':
from wiz_remediation_core.response_function_api import GCPTargetResource
args = GCPRemediationArgs(triggered_rule_id="", target_resource=GCPTargetResource(project_id="amirproject-381814", resource_name="lior-instance",region="us-central1", resource_id="https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/amirproject-381814/zones/us-central1-b/instances/lior-instance"))
print(remediate(args))
Post Containment Assessment
Following containment, Wiz Defend, integrated with Wiz Cloud, facilitated post-incident security posture assessment, identifying the root cause and attack entry points:
- The instance was publicly exposed, increasing its risk of exploitation.
- Vulnerabilities in cloud workloads were flagged, enabling security teams to apply targeted remediation.
- Attack path analysis revealed that the compromised instance had access to sensitive cloud resources, necessitating further security hardening.
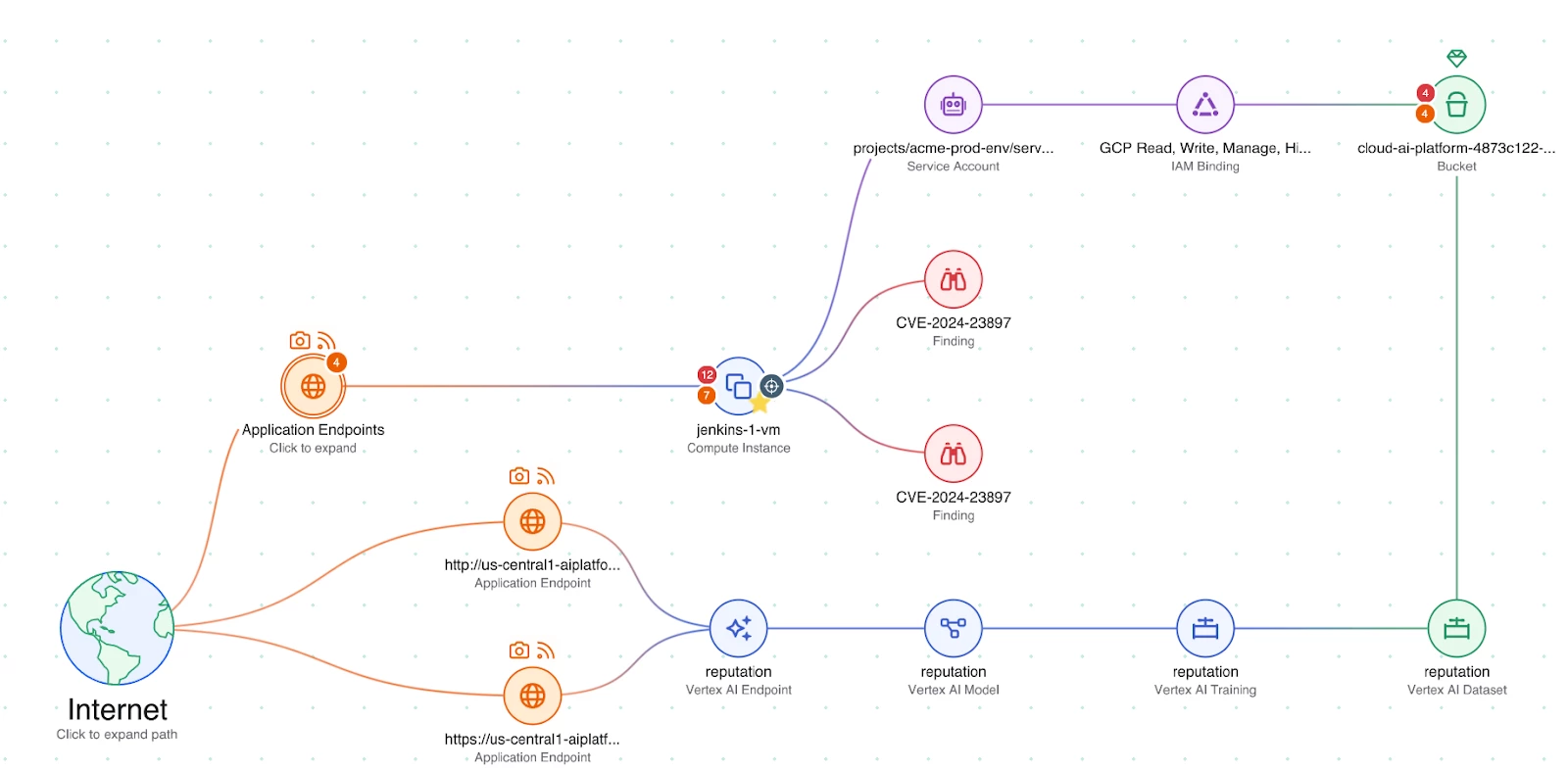
Figure: Attack path analysis
Wiz maps the attack progression, showing:
- Initial Access: Exploitation of a Jenkins vulnerability on a publicly exposed VM.
- Execution: Code execution via CVE-2024-23897 using publicly available exploits.
- Privilege Escalation & Lateral Movement: The compromised service account had high Kubernetes and data access privileges.
- Impact: Access to AI training data, potentially compromising AI model integrity.
Wiz provides automated remediation strategies, including:
- Patch Management: Guidance to fix CVE-2024-23897 via gcloud CLI, Google Cloud Console, Terraform, and automated scripts.
- Access Control Improvements: Restricting VM exposure, enforcing least privilege access, and securing AI data.
Summary
This use case demonstrates how Wiz Defend streamlines the entire incident response lifecycle—from threat detection to investigation, containment, and security posture improvement:
- Detect & Respond: Quickly identify, investigate, and contain cloud threats.
- Analyze & Strengthen: Understand attack paths, assess security posture, and mitigate risks.
- Remediate & Prevent: Generate step-by-step remediation procedures to prevent recurrence and enhance cloud security resilience.
Use Case 2: Unauthorized Service Account Impersonation & Data Exposure
Service account misconfigurations and privilege escalations pose a significant risk in cloud environments, potentially leading to data exposure, unauthorized access, and persistence by threat actors. Without continuous monitoring and real-time detection, adversaries can exploit these vulnerabilities to escalate privileges and exfiltrate sensitive data.
Wiz Defend provides advanced threat detection and automated response capabilities to quickly identify and mitigate such risks before they lead to business impact.
Threat Detection
In this example, Wiz Defend detected suspicious activities by the service account iam-runner@acme-prod-env.iam.gserviceaccount.com, triggering a high-severity threat alert. Wiz Defend groups detections into one incident.
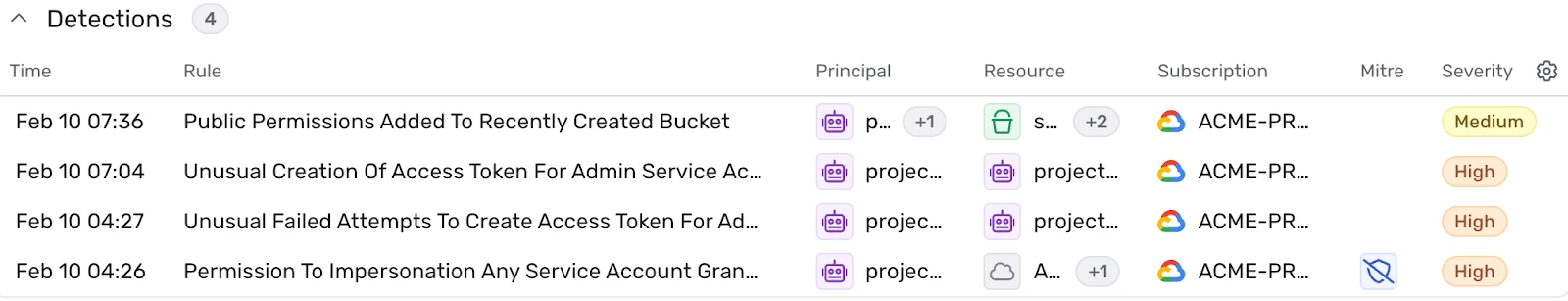
Figure: security alerts triggered by suspicious activities
- Granted public access to three newly created storage buckets.The roles/storage.objectViewer permission was assigned to allUsers, making the stored data publicly accessible.
- Generated access tokens for the high-privilege admin service account logs-admin@acme-prod-env.iam.gserviceaccount.com after an initial failed attempt.
- Granted itself the roles/iam.serviceAccountTokenCreator role, allowing impersonation of any service account within the acme-prod-env project.
These activities suggested a coordinated attempt at data exfiltration and privilege escalation, triggering multiple high-severity detections in Wiz Defend.
Investigation & Threat Analysis
- Storyline & Investigation Graph: Wiz Defend analyzes logs from cloud, SaaS, IdP, VCS, and compute workloads to correlate suspicious activities into a cohesive Threat Storyline, allowing faster and more precise response.
- Wiz Defend visualizes the attack path, detailing suspicious processes, origin IPs, affected resources, and security risks.
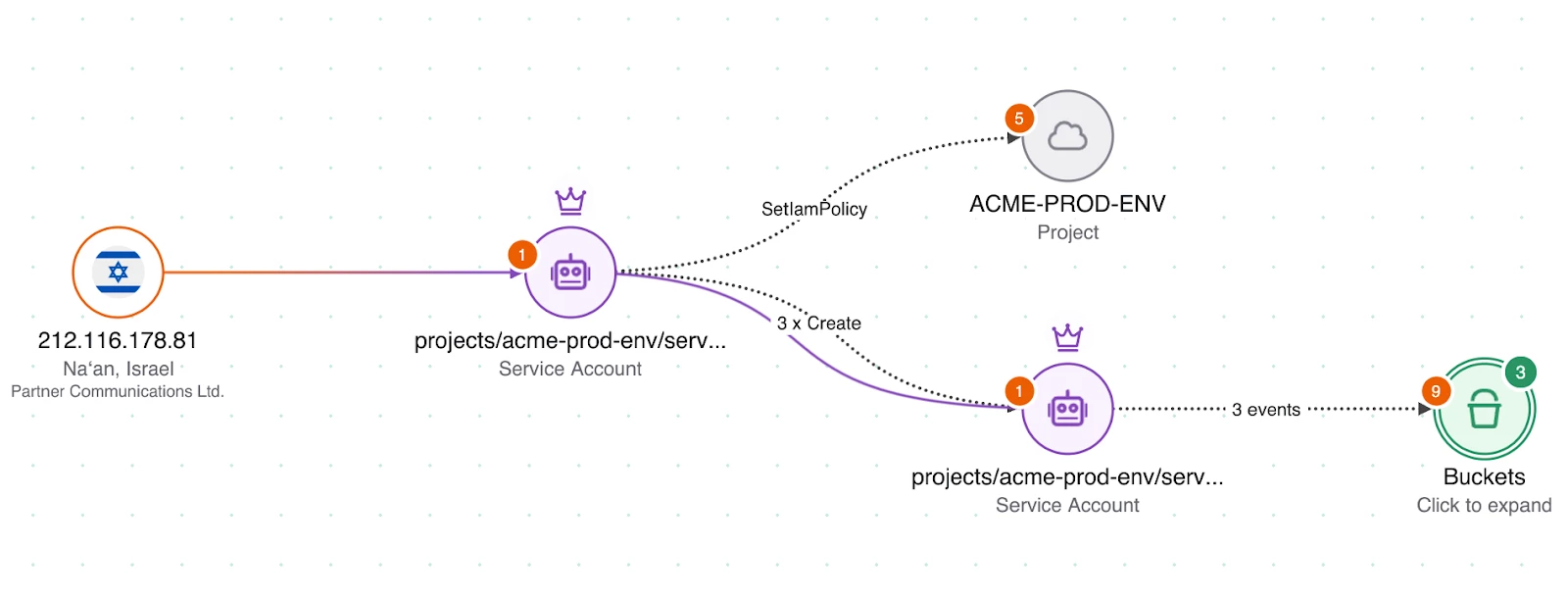
Figure: Attack path
- Threat Timeline: An interactive timeline provides a clear sequence of events, helping pinpoint the root cause and assess the full attack scope.
Incident Response & Containment Actions
To mitigate the risk, Wiz Defend provides one-click response actions, including:
- For the compromised service accounts:
- Revoke the roles/iam.serviceAccountTokenCreator role to prevent further impersonation.
- Disable the service account to halt malicious activity.
- For the exposed storage buckets:
- Remove public access permissions.
- Restrict access to authorized identities only.
Post Containment Assessment
After containment, Wiz Defend, integrated with Wiz Cloud, helps assess the security posture and identify the full impact of the incident. Wiz identified compromised service account, data resource can be reached by this service account, other accounts can be impersonated:
- Data at Risk: The service account had access to sensitive cloud storage, logs, and application data.
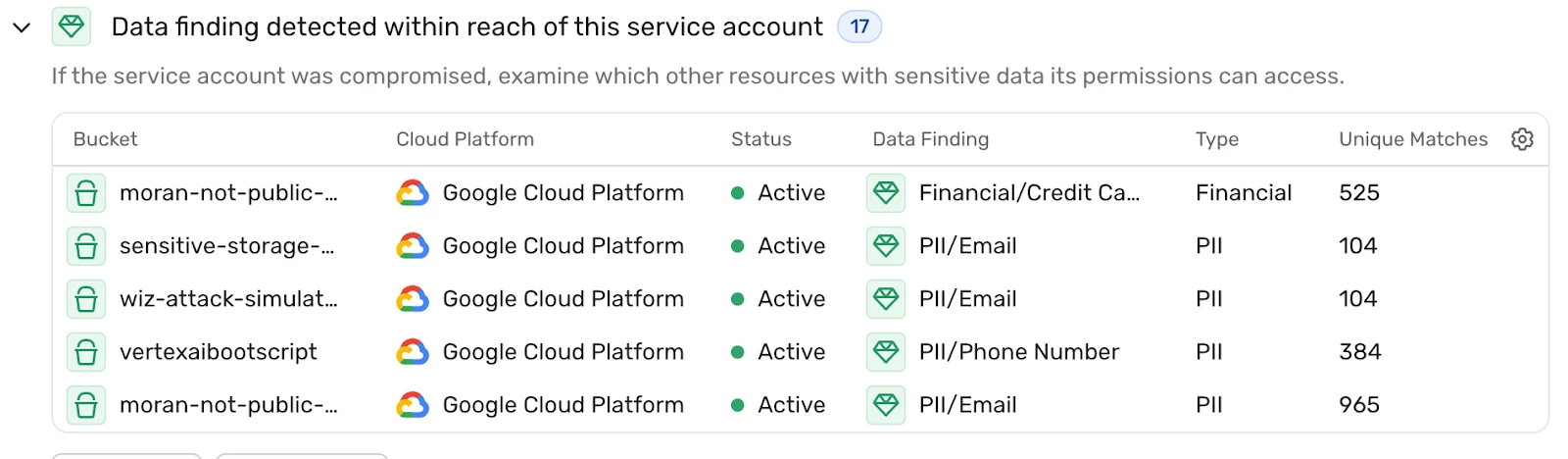
Example: service accounts that have access to sensitive data
- Impersonation Risks: The service account could impersonate multiple high-privilege accounts, increasing the potential damage.
Wiz Defend also facilitated a comprehensive security posture assessment, identifying misconfigurations that contributed to the attack:
- Publicly accessible storage buckets that contained sensitive data.
- Over-privileged service accounts with unnecessary permissions.
- Unrestricted service account impersonation, increasing lateral movement risk.
Wiz Defend provided automated remediation guidance, recommending:
- Tightening IAM policies to enforce the principle of least privilege.
- Implementing conditional access controls to prevent unauthorized impersonation.
- Using workload identity federation to reduce reliance on long-lived service account credentials.
Summary
This use case demonstrates how Wiz Defend delivers end-to-end cloud threat detection and response, enabling security teams to quickly detect privilege escalations, investigate data exposure risks, and take immediate action to mitigate threats. By proactively securing service accounts and enforcing least privilege, organizations can prevent unauthorized access and strengthen their cloud security posture against evolving threats.
What's next
- Learn more about Wiz and Google Cloud
- Learn more about how to See and secure your Google Cloud environment with Wiz
- Read the Wiz Solution Briefing for Google Cloud.


